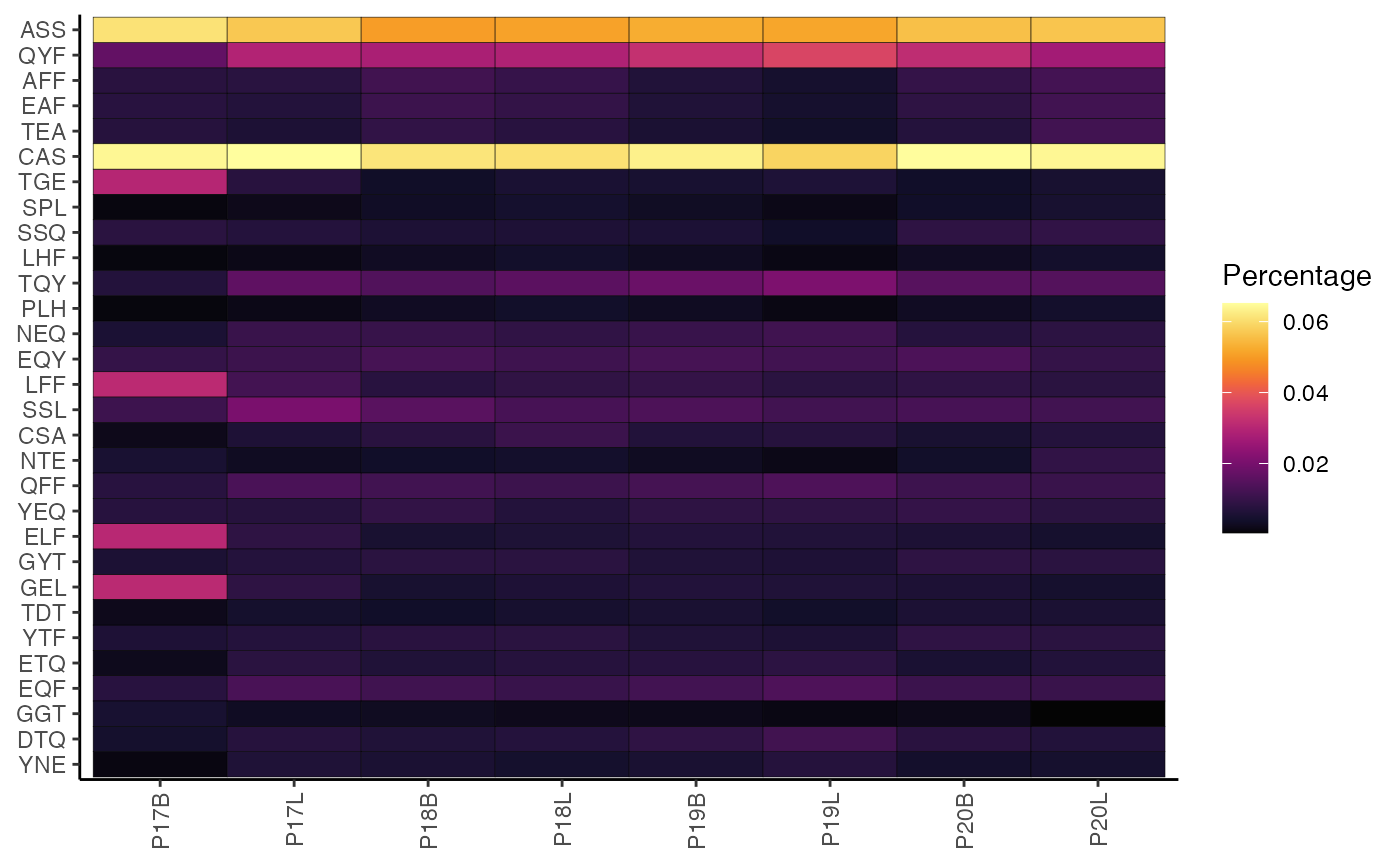
This function calculates and visualizes the frequency of k-mer motifs for either nucleotide (nt) or amino acid (aa) sequences. It produces a heatmap showing the relative composition of the most variable motifs across samples or groups.
percentKmer(
input.data,
chain = "TRB",
cloneCall = "aa",
group.by = NULL,
order.by = NULL,
motif.length = 3,
min.depth = 3,
top.motifs = 30,
exportTable = FALSE,
palette = "inferno",
...
)Arguments
- input.data
The product of
combineTCR(),combineBCR(), orcombineExpression()- chain
The TCR/BCR chain to use. Accepted values:
TRA,TRB,TRG,TRD,IGH, orIGL(for both light chains).- cloneCall
Defines the clonal sequence grouping. Accepted values are:
nt(CDR3 nucleotide sequence) oraa(CDR3 amino acid sequence).- group.by
A column header in the metadata or lists to group the analysis by (e.g., "sample", "treatment"). If
NULL, data will be analyzed as by list element or active identity in the case of single-cell objects.- order.by
A character vector defining the desired order of elements of the
group.byvariable. Alternatively, usealphanumericto sort groups automatically.- motif.length
The length of the kmer to analyze
- min.depth
Minimum count a motif must reach to be retained in the output (
>= 1). Default:3.- top.motifs
Return the n most variable motifs as a function of median absolute deviation
- exportTable
If
TRUE, returns a data frame or matrix of the results instead of a plot.- palette
Colors to use in visualization - input any hcl.pals
- ...
Additional arguments passed to the ggplot theme
Value
A ggplot object displaying a heatmap of motif percentages.
If exportTable = TRUE, a matrix of the raw data is returned.
Details
The function first calculates k-mer frequencies for each sample/group. By default, it then identifies the 30 most variable motifs based on the Median Absolute Deviation (MAD) across all samples and displays their frequencies in a heatmap.
Examples
# Making combined contig data
combined <- combineTCR(contig_list,
samples = c("P17B", "P17L", "P18B", "P18L",
"P19B","P19L", "P20B", "P20L"))
# Using percentKmer()
percentKmer(combined,
chain = "TRB",
motif.length = 3)